Phases of Vulnerability Analysis
A comprehensive guide to the phases of vulnerability analysis, detailing each step from planning to remediation in the vulnerability management lifecycle.
Phases of Vulnerability Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
Vulnerability analysis is a cornerstone of effective cybersecurity. Without a clear understanding of your network’s weaknesses, you can’t protect your assets or respond to threats. This guide breaks down the vulnerability assessment process into actionable phases, providing practical steps and tips for each stage.
Why Conduct Vulnerability Assessments?
- Identify unknown weaknesses: You can’t fix what you don’t know exists.
- Prioritize security efforts: Focus on the most critical vulnerabilities first.
- Meet compliance requirements: Many regulations require regular assessments.
- Protect business assets: Reduce the risk of breaches and data loss.
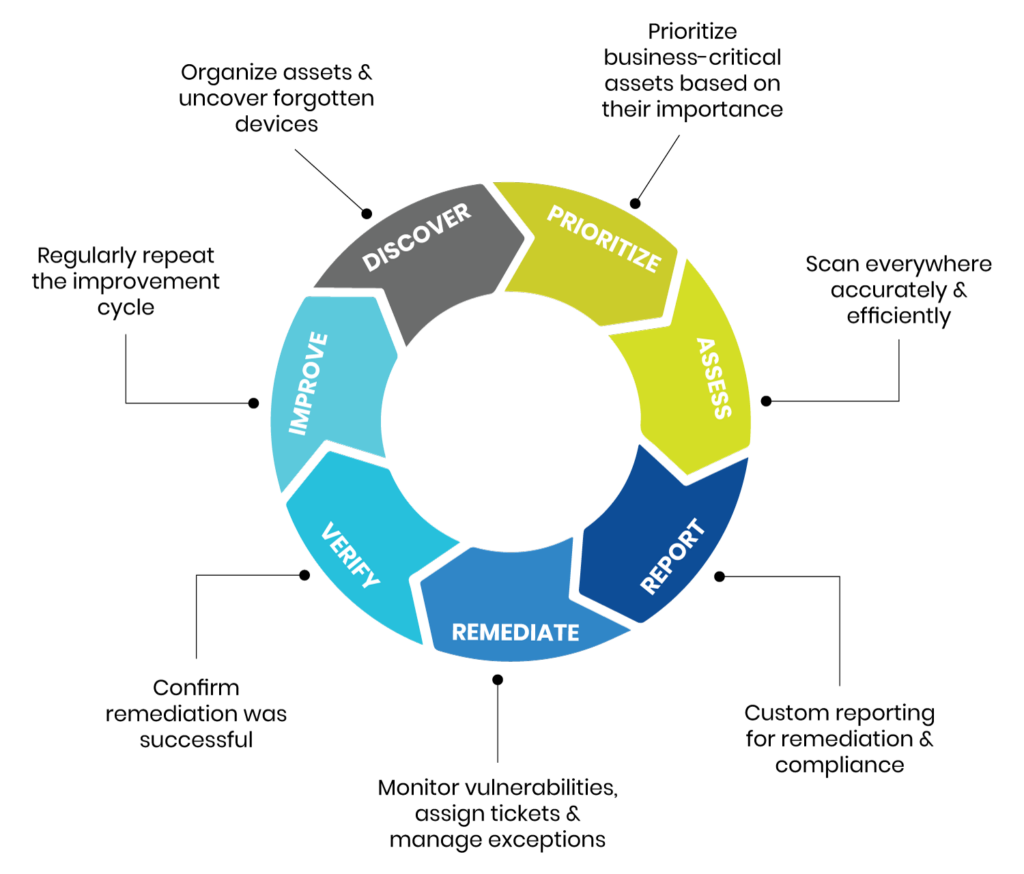
The 7 Phases of Vulnerability Analysis
1. Define Parameters and Plan Assessment
Before scanning, set the foundation for your assessment:
- Determine scope: Identify which assets (hardware, software, devices, cloud resources) will be assessed.
- Asset discovery: Catalog all devices and applications, including BYOD and IoT.
- Set baselines: Understand current configurations, permissions, and risk tolerance.
- Assign roles: Decide who will conduct the assessment and who needs to be involved.
- Select tools: Choose appropriate vulnerability scanners and management tools.
- Schedule: Establish timelines for assessment and remediation.
Tip: Use automated asset discovery tools to simplify inventory management.
2. Scan Network for Vulnerabilities
With your plan in place, begin scanning:
- Automated vs. manual: Use automated scanners for efficiency, but supplement with manual checks when needed.
- Leverage threat intelligence: Cross-reference findings with vulnerability databases.
- Filter false positives: Not every finding is a real risk.
Expect to find many vulnerabilities, especially during your first assessment.
3. Analyze Results
Turn raw scan data into actionable insights:
- Assess severity: Evaluate the criticality and exploitability of each vulnerability.
- Consider impact: Identify which business processes or data could be affected.
- Correlate data: Combine scan results with logs, penetration tests, and other sources.
Clear analysis helps communicate risks to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
4. Prioritize Vulnerabilities
Not all vulnerabilities are equal:
- Critical first: Address vulnerabilities that are actively exploited or pose the highest risk.
- Future threats: Next, focus on those with known exploits or high potential impact.
- Plan remediation: Create a prioritized action list.
Prioritization ensures resources are used effectively and the biggest risks are addressed first.
5. Create the Vulnerability Assessment Report
Document your findings for action and accountability:
- Detail vulnerabilities: Include severity, affected assets, and potential attack vectors.
- Recommend solutions: Suggest patches or mitigation strategies.
- Visualize data: Use charts and summaries for executive audiences.
- Technical appendix: Provide detailed instructions for IT and security teams.
A clear report bridges the gap between technical teams and business leaders.
6. Use Results to Inform Remediation and Mitigation
Move from analysis to action:
- Patch critical issues: Apply fixes where available.
- Mitigate where needed: Use workarounds or compensating controls if patches aren’t possible.
- Track progress: Monitor remediation efforts and update stakeholders.
Regularly revisit your assessment to ensure all prioritized vulnerabilities are addressed.
7. Regularly Repeat Vulnerability Assessments
Security is an ongoing process:
- Continuous improvement: New vulnerabilities emerge as your network evolves.
- Schedule regular scans: Monthly, quarterly, or after major changes.
- Update tools and processes: Stay current with the latest threats and technologies.
Frequent assessments help maintain a strong security posture.
Best Practices for Using Vulnerability Assessment Tools
- Check existing solutions: Your current cybersecurity suite may include assessment tools.
- Choose the right format: Ensure tools are compatible with your environment (on-premises, cloud, hybrid).
- Use multiple tools: Combine commercial and open-source scanners for broader coverage.
- Integrate with workflows: Connect assessment tools to ticketing and ITSM systems for streamlined remediation.
Should Every Organization Run Vulnerability Assessments?
Absolutely. Regardless of size or industry:
- All networks are targets: Even small businesses face cyber threats.
- Compliance matters: Regulations like HIPAA and GDPR require regular assessments.
- Affordable options exist: Free and open-source tools can help organizations with limited budgets.
Investing in vulnerability assessments can prevent costly breaches and protect your reputation.
Bottom Line
Vulnerability assessments are like regular health checkups for your network. They help you find and fix weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. By following a structured process and leveraging the right tools, you can strengthen your security posture and safeguard your business assets.