A Beginner's Guide to Steganography
Techniques and Tools for Concealing Data within Digital Media
What is Steganography?
Cryptography is about scrambling a message so no one can read it. Steganography is about hiding the message so no one even knows it exists.
Imagine you want to send a secret letter to a friend.
- Cryptography: You write the letter in a secret code. If a guard finds it, they know it’s a secret, even if they can’t read it.
- Steganography: You write the letter in invisible ink on the back of a grocery list. The guard sees the grocery list and lets it pass, having no idea a secret message is even there.
In the digital world, we hide secrets inside Images (.jpg), Audio (.mp3), or even Videos.
How it Works: The Magic of “LSB”
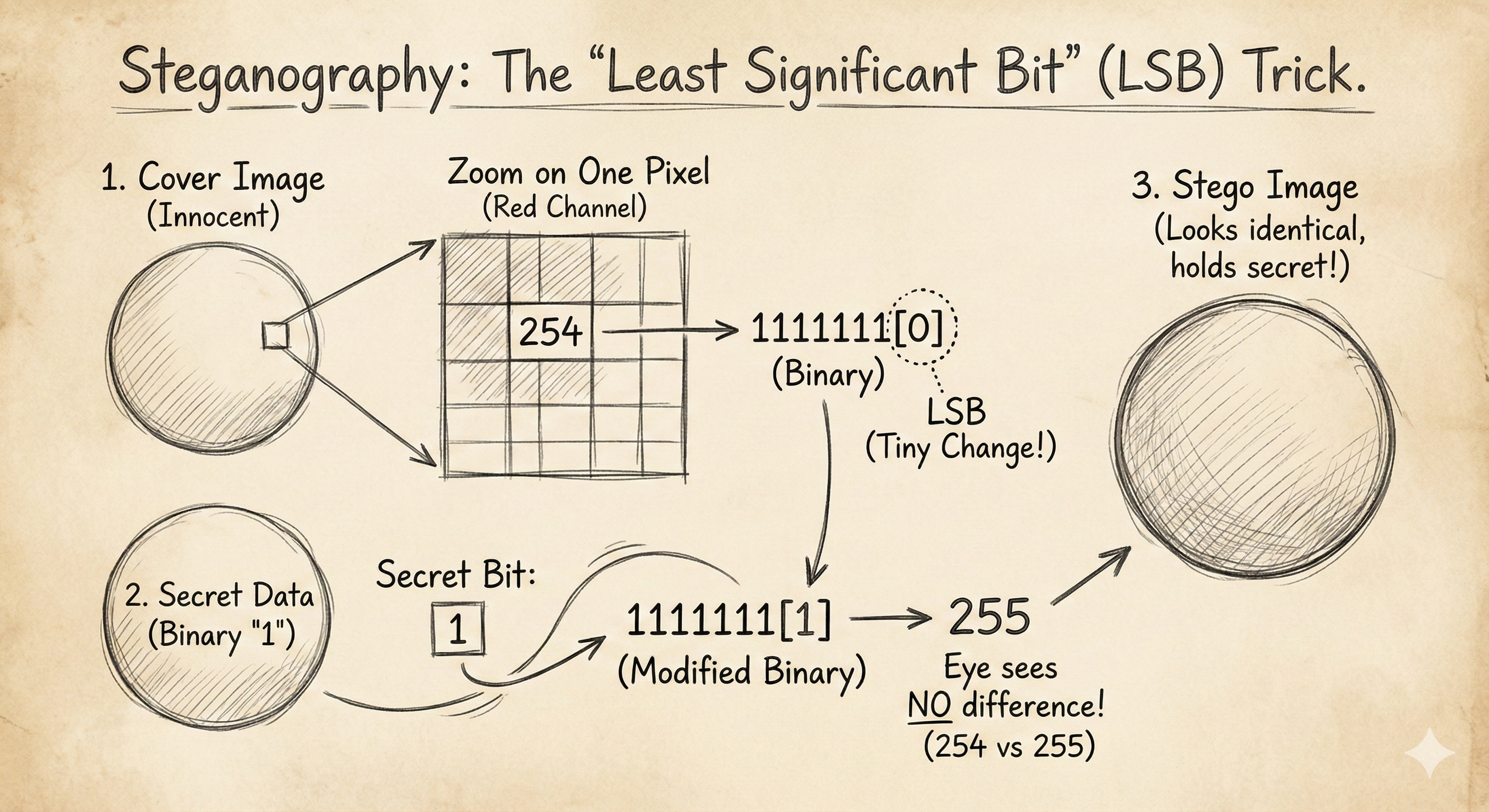
The most common technique is Least Significant Bit (LSB) modification. To understand this, you just need to know how computers store color.
Every pixel in an image is made of 3 colors: Red, Green, Blue (RGB). Each color is a number from 0 to 255 (8 bits of data).
Let’s look at one red pixel. In binary, the number 255 looks like 11111111.
- The bit on the far left is the Most Significant Bit (MSB). If you change it to
0, the number becomes01111111(127). The color changes drastically (bright red to dark red). - The bit on the far right is the Least Significant Bit (LSB). If you change it from
1to0(11111110), the number becomes 254.
The Trick: The human eye cannot see the difference between Red value 255 and Red value 254. They look identical.
So, we can replace that last bit of every pixel with our secret data. We are effectively “painting” our secret message into the invisible noise of the image.
The Tools (CEH Lab Standard)
You don’t need to code this manually. There are standard tools used in the CEH exam and real life.
1. Steghide (The Classic)
This is a command-line tool for Linux/Windows.
To Hide Data:
1
2
3
# Syntax: steghide embed -cf [Cover File] -ef [Secret File]
steghide embed -cf innocent_puppy.jpg -ef secret_passwords.txt
- It will ask for a passphrase. Even if someone suspects steganography, they can’t extract the data without this password.
To Extract Data:
1
2
steghide extract -sf innocent_puppy.jpg
2. OpenStego (The GUI)
For those who prefer clicking buttons, OpenStego is a free tool that does the same thing. You select your “Cover File” (the image), your “Secret File”, and click “Hide”.
Why Do Hackers Use This?
- Exfiltration: An attacker breaks into a company and steals a database. If they send a 50MB file called
passwords.sqlout of the network, the firewall will block it.- The Fix: They hide the data inside the company logo on the public website or seemingly harmless employee profile photos. The firewall just sees “images” leaving the network, which is normal.
- C2 Communication: Malware can download a “meme” from Twitter. Hidden inside that meme are the commands the malware needs to run (e.g., “Delete all files”). The Antivirus sees a meme; the malware sees a command.
How to Detect It (Steganalysis)
If the human eye can’t see it, how do we catch it?
- File Size: If a simple 500x500 pixel JPEG is 50MB in size, something is wrong.
- Hex Editors: Opening the image in a Hex Editor might reveal readable text hidden at the very end of the file.
- Statistical Attacks: Tools like
StegExposeanalyze the statistical distribution of colors. Natural photos have “noise.” Steganography creates mathematical patterns that look “too perfect” or “too random” to a computer.
Summary for the Exam
- Steganography: Hiding the existence of data.
- Cover Object: The innocent file (image/audio) holding the data.
- Stego Object: The file after it has the secret data inside.
- LSB: The most common technique (modifying the last bit).